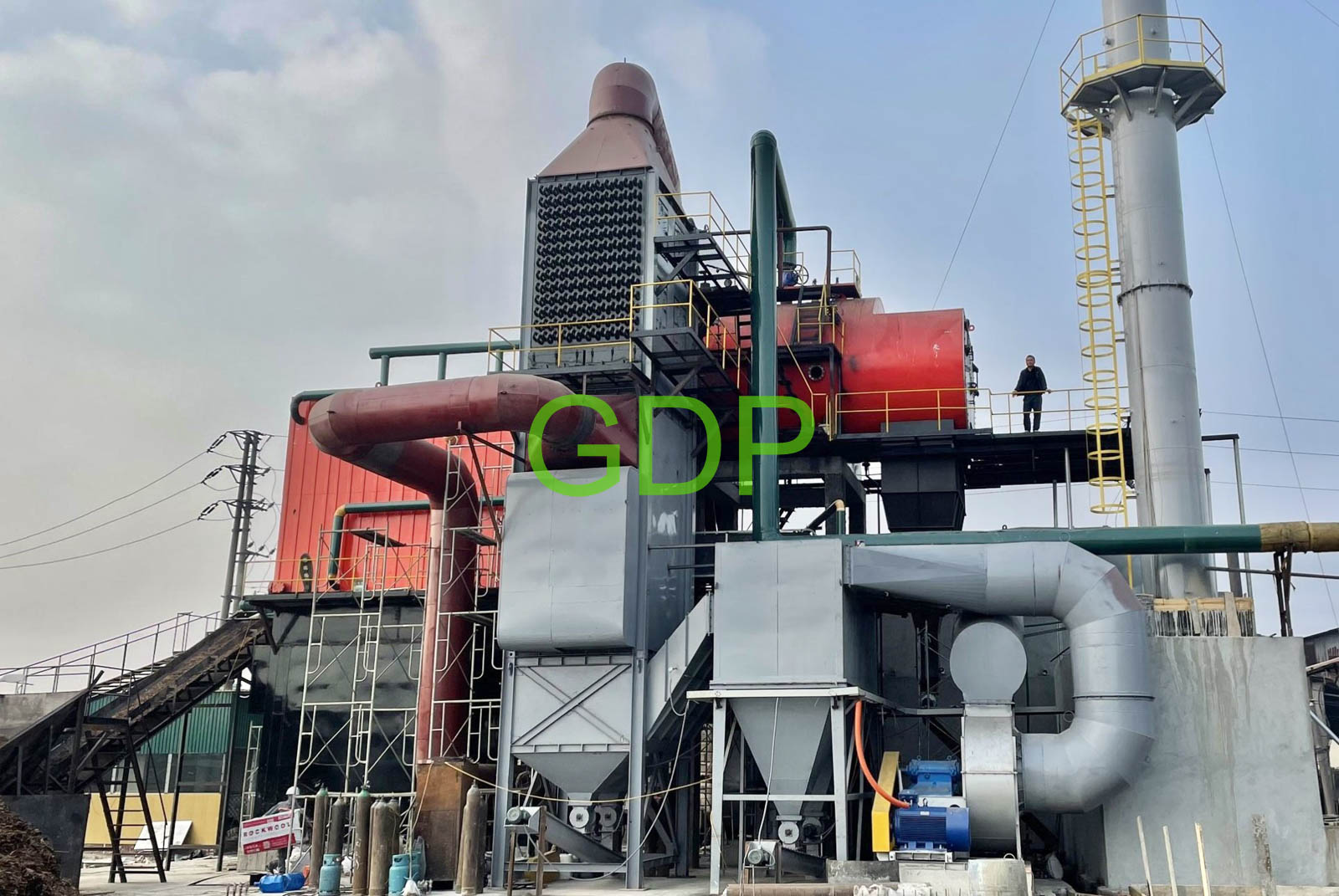
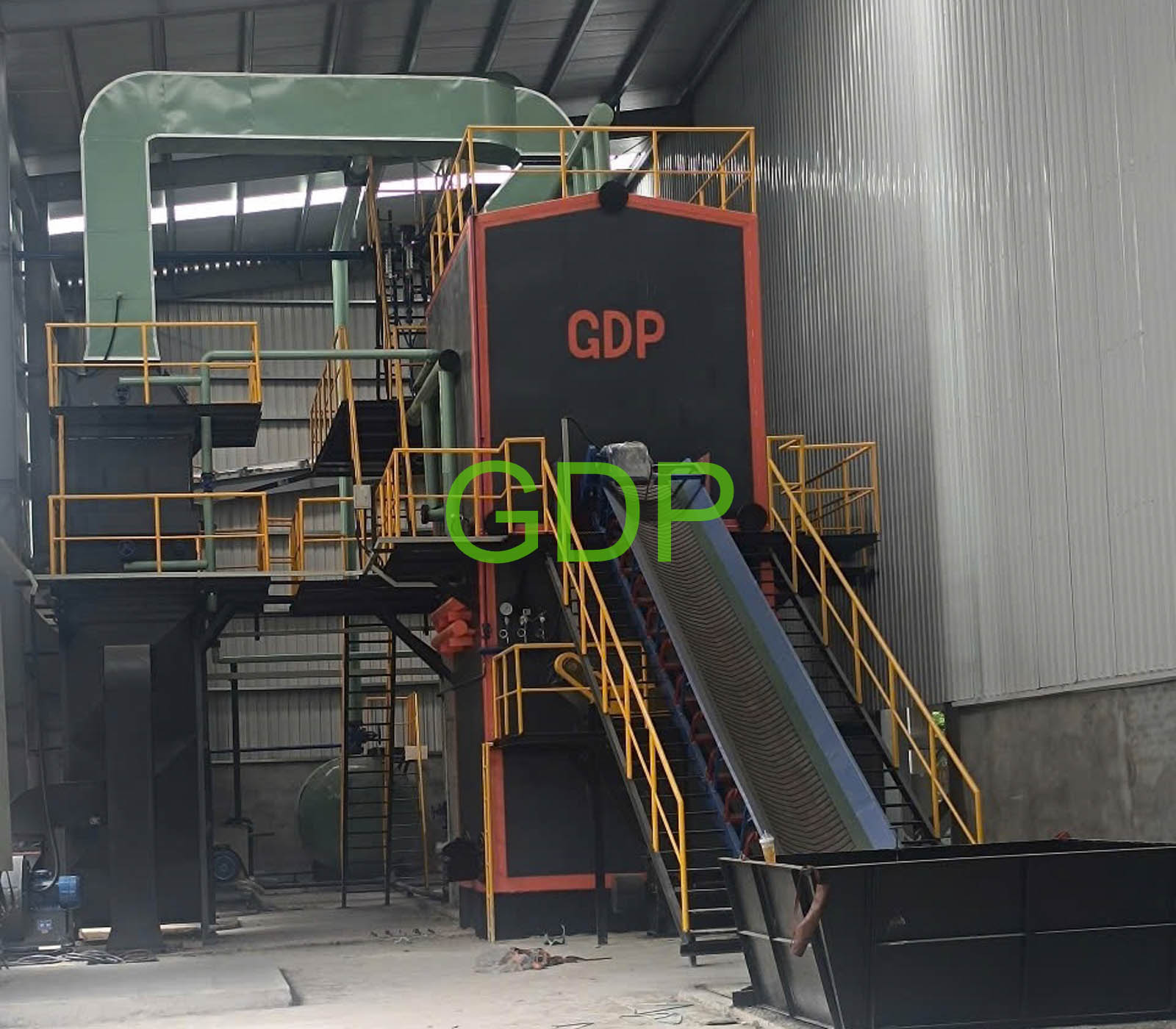
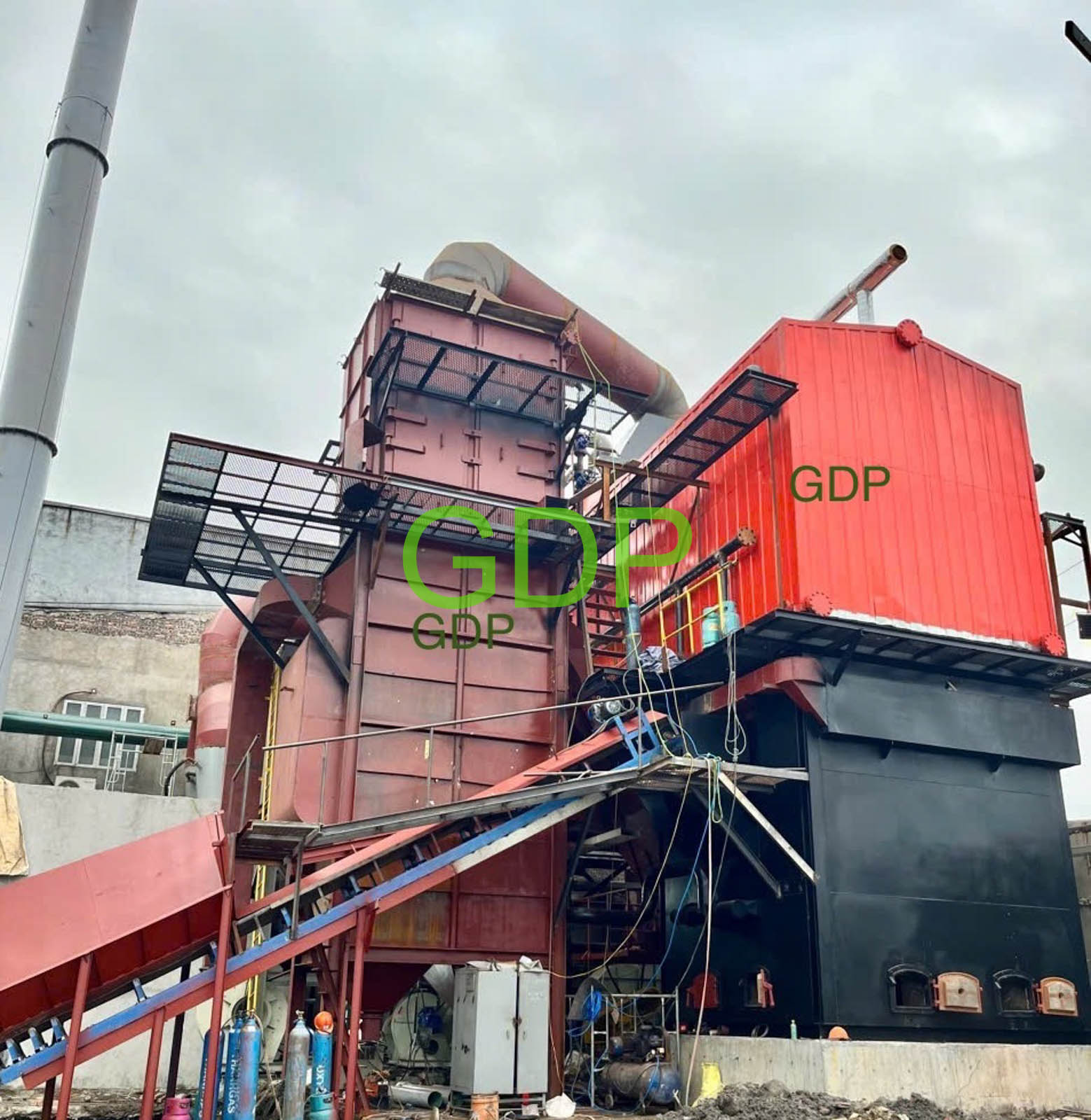
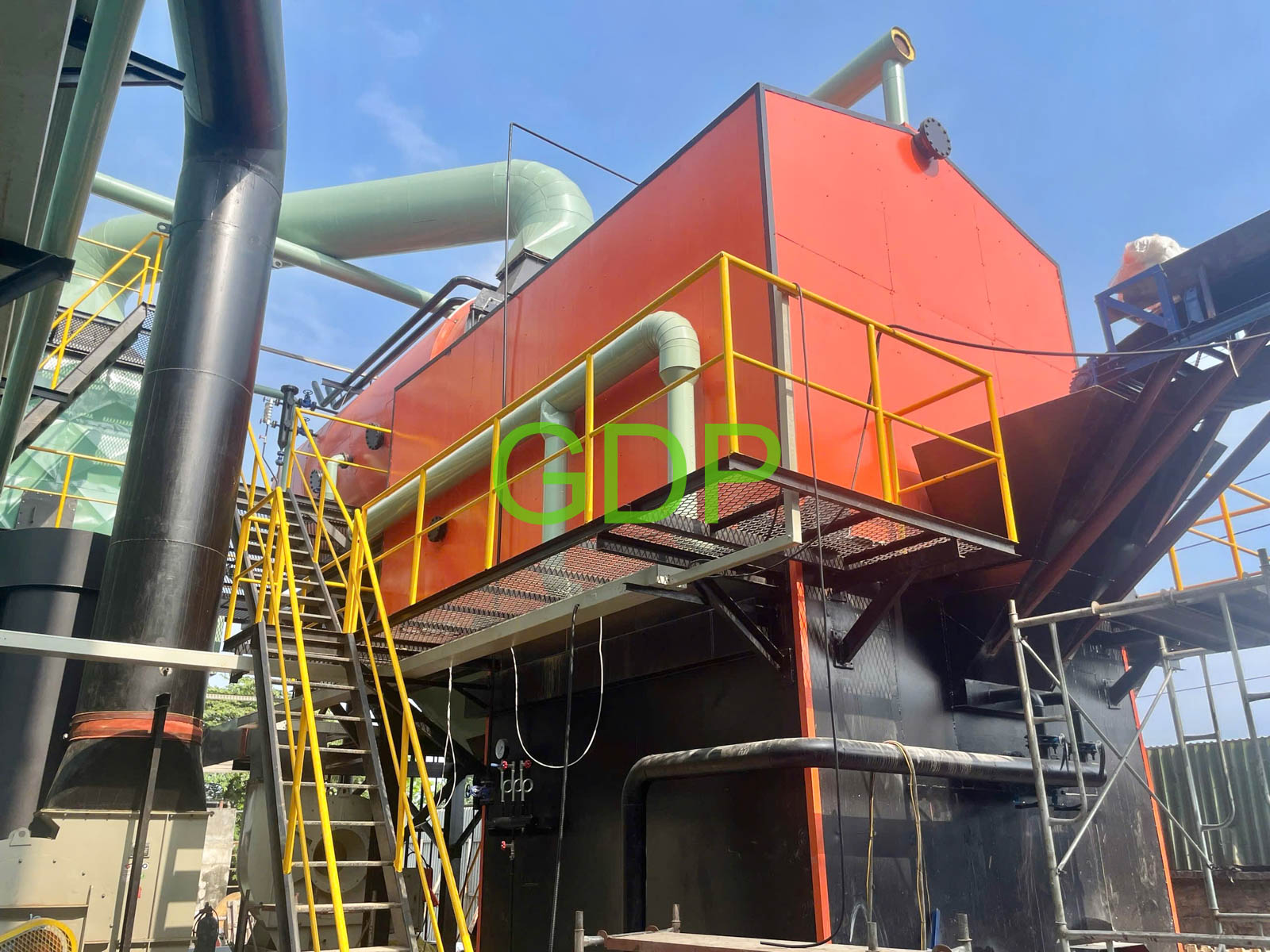
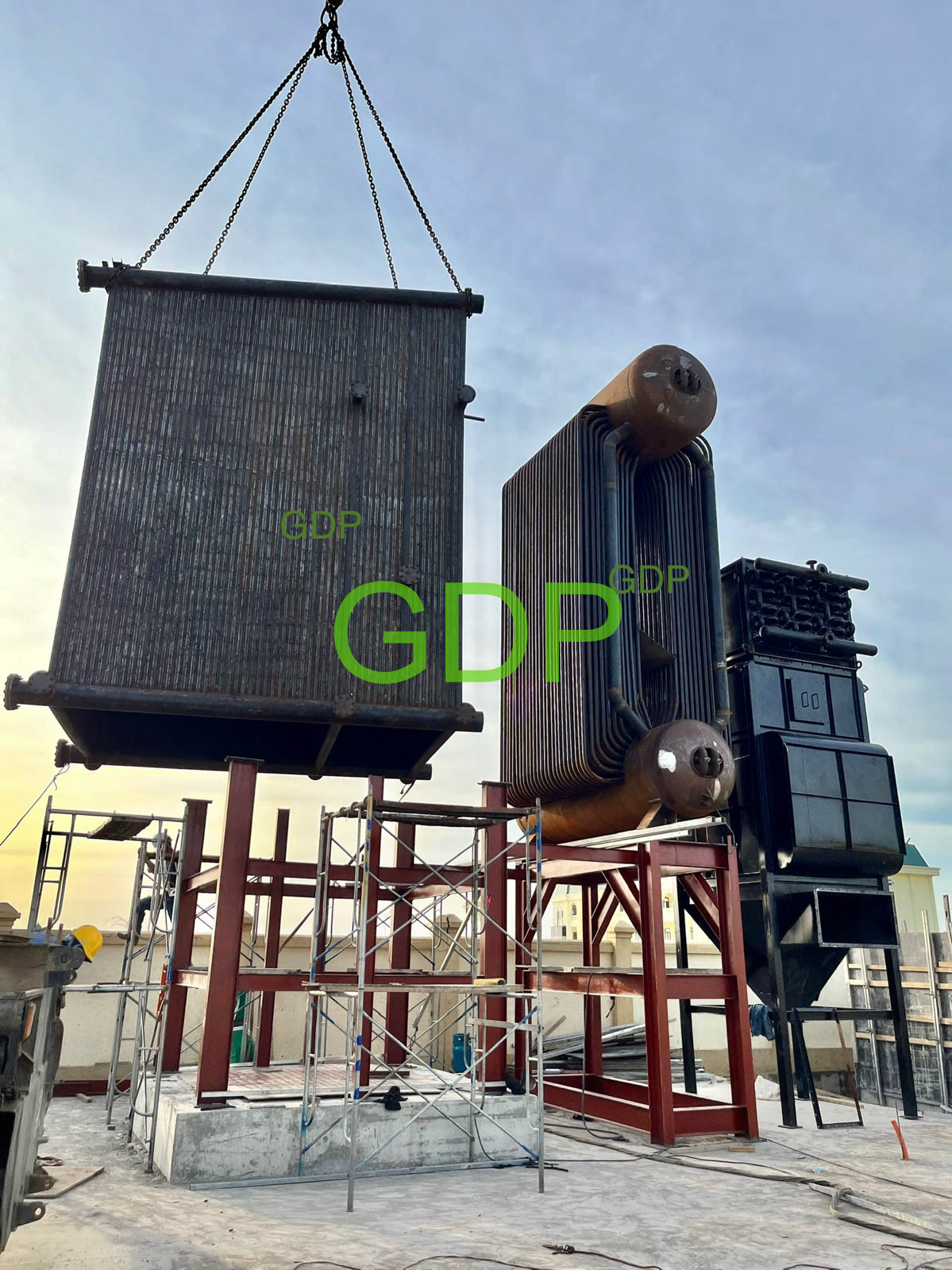
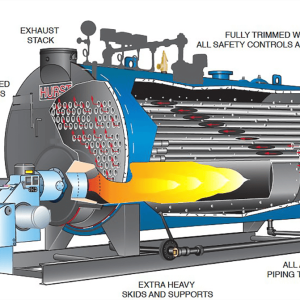
A combined water-tube and fire-tube fluidized bed boiler integrates the characteristics of both water-tube and fire-tube designs, along with fluidized bed combustion technology, to enhance efficiency and flexibility in steam generation. This type of boiler utilizes water tubes for radiant heat transfer from the combustion zone and fire tubes for convective heat transfer, while the fluidized bed ensures efficient combustion and fuel utilization.

-
Integrated Design:
Combines the benefits of both water-tube and fire-tube designs, offering a balance of radiant and convective heat transfer.
-
Fluidized Bed Combustion:
Employs a fluidized bed for efficient combustion of various fuels, including biomass and low-grade fuels, with improved emissions control.
-
High Efficiency:
The combination of water tubes, fire tubes, and fluidized bed combustion leads to higher overall thermal efficiency compared to traditional boiler designs.
-
Fuel Flexibility:
Fluidized bed technology allows for the combustion of a wide range of fuels, including those with high ash content or moisture.
-
Improved Load Following:
The boiler can handle fluctuations in steam demand more effectively due to the characteristics of both water-tube and fire-tube sections.
-
Reduced Emissions:
Fluidized bed combustion, combined with proper design and operation, can lead to lower emissions of pollutants like NOx and SOx.
-
1. Fluidized Bed:
Fuel and bed material (like sand) are suspended in a hot, bubbling bed by jets of air.
-
2. Combustion:
Combustion occurs within the fluidized bed, with the hot gases rising through the boiler.
-
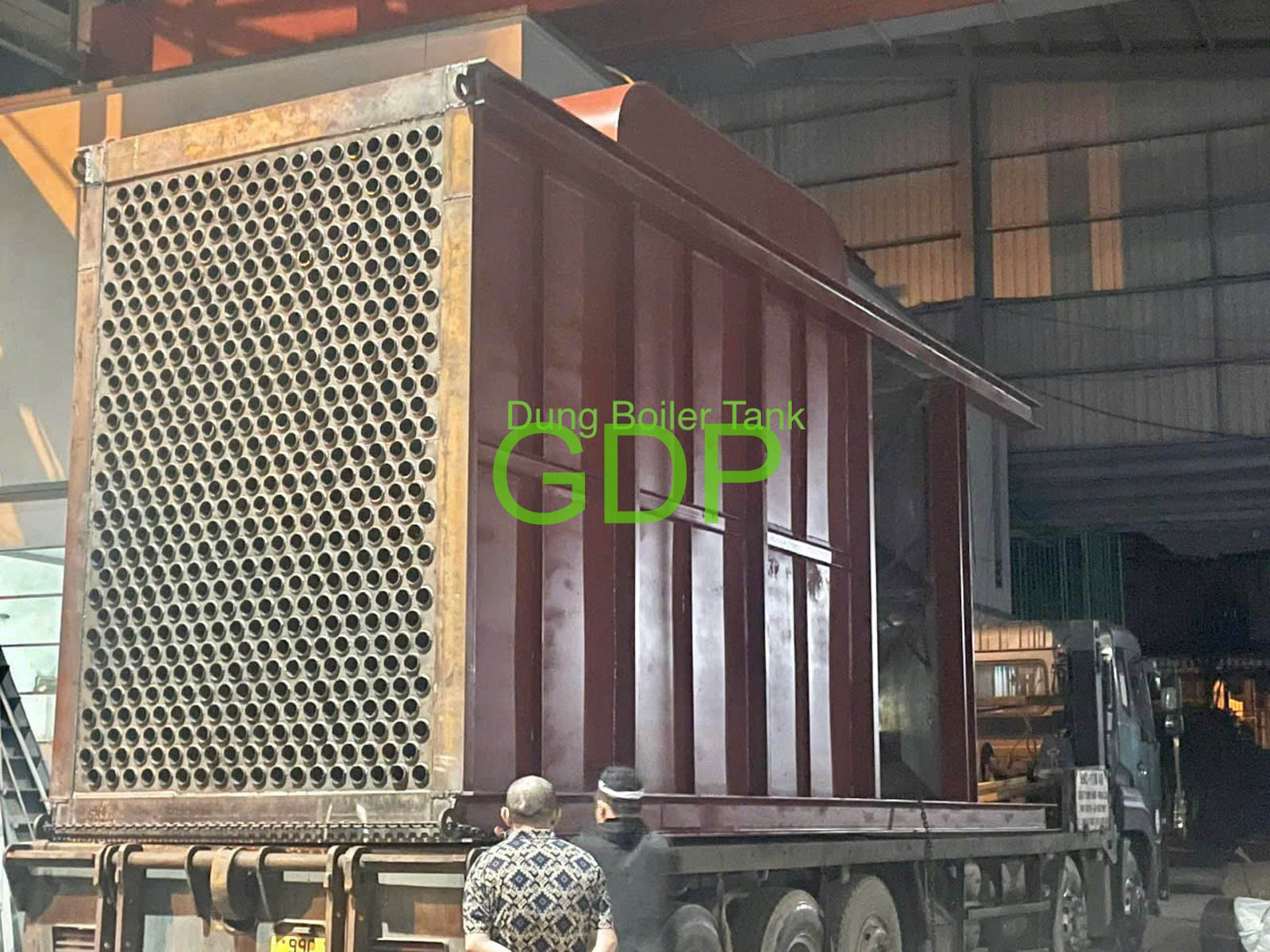
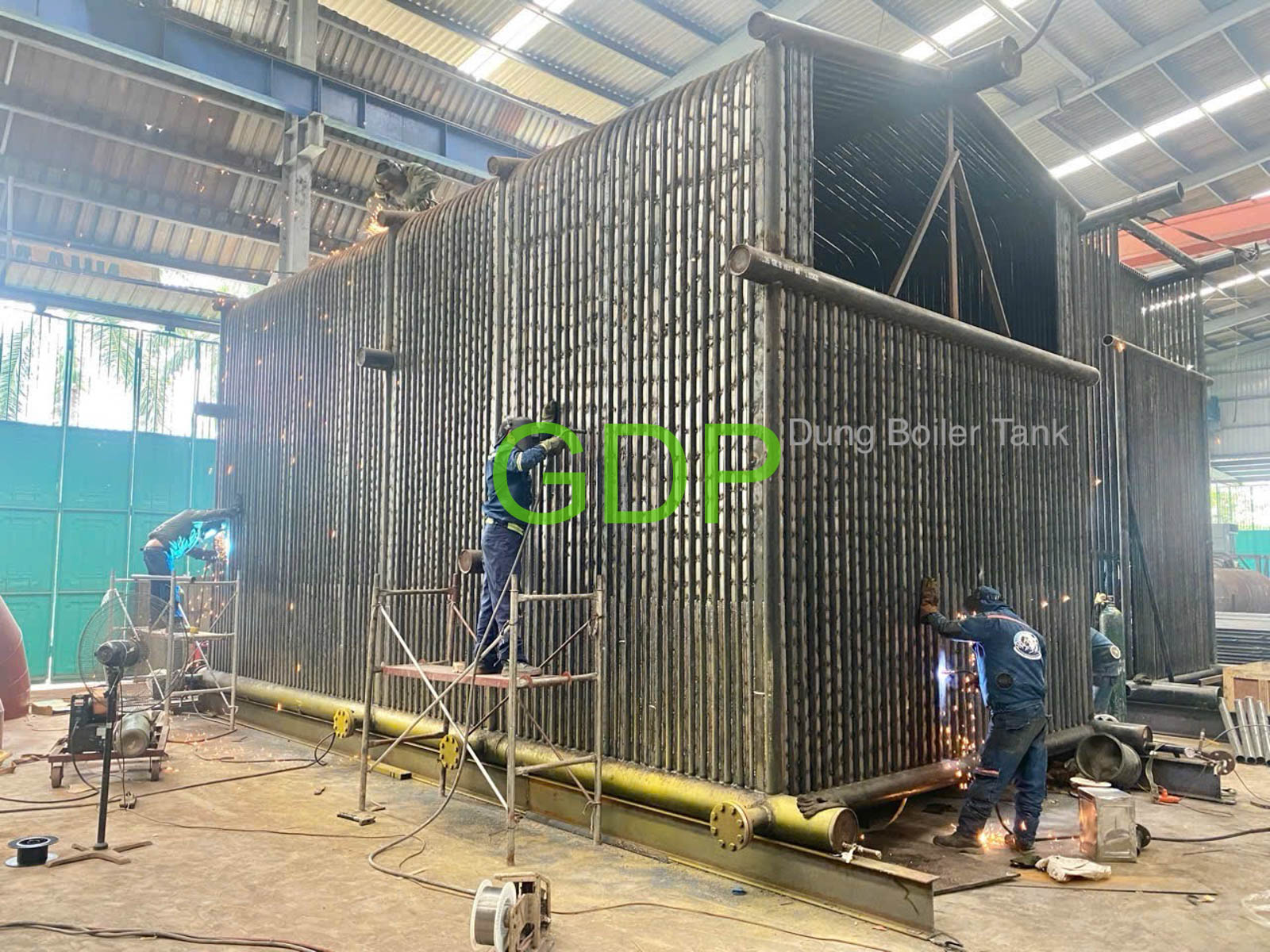
3. Water Tubes:
Water-filled tubes are strategically placed within the furnace and around the combustion zone to absorb radiant heat.
-
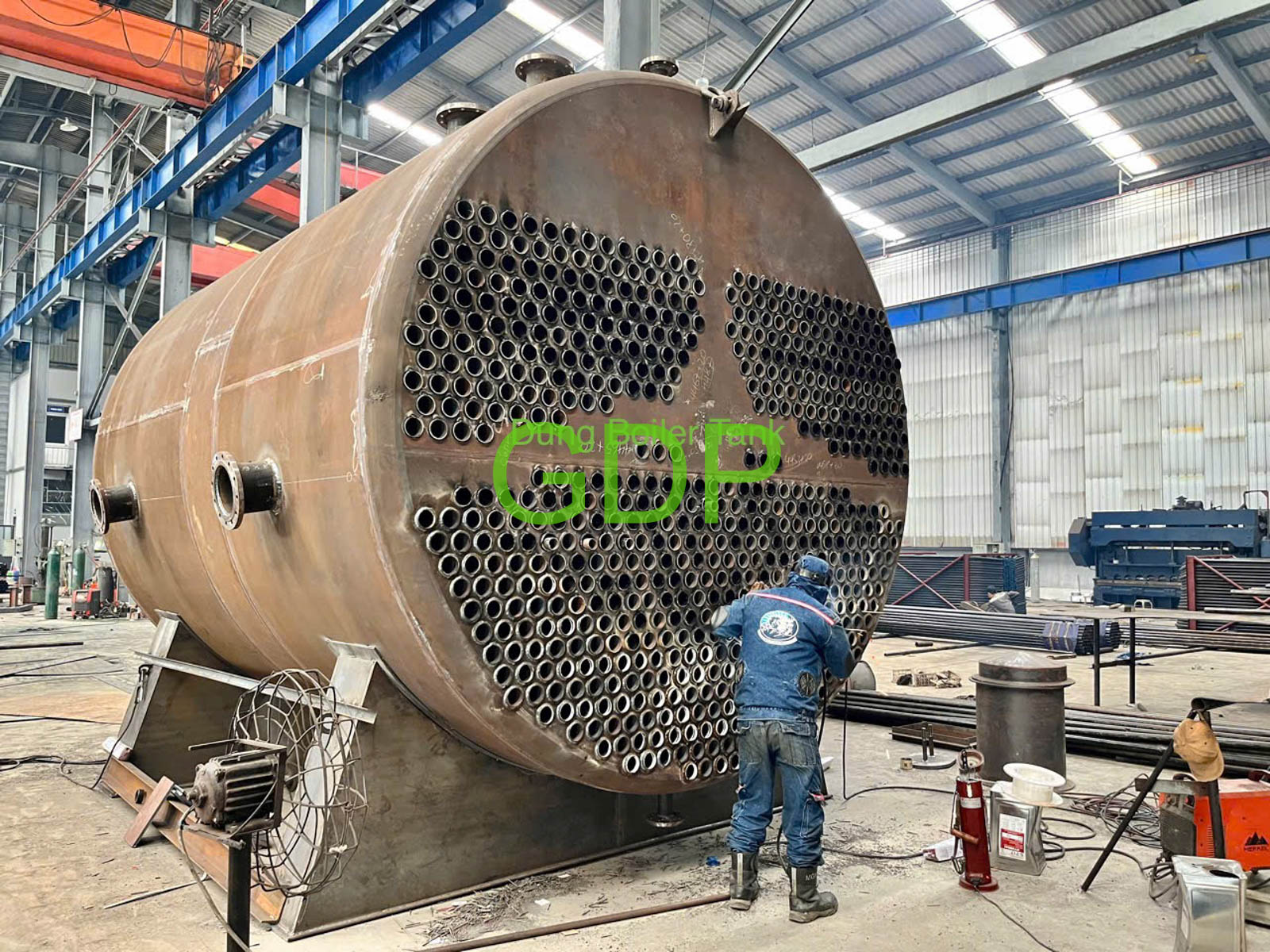
4. Fire Tubes:
Hot flue gases pass through fire tubes, which are submerged in water, to provide additional convective heat transfer.
-
5. Steam Generation:
The heat absorbed by the water in both water tubes and fire tubes converts the water into steam.

































Đặt câu hỏi