Currently, manufacturing plants have high demand for heat in technological processes. Typically, this heat source will be produced and distributed through a common heating device – the boiler. However, in reality, there are products with superior features. That is the thermal oil furnace. Let’s find out with GDP Group through this article.
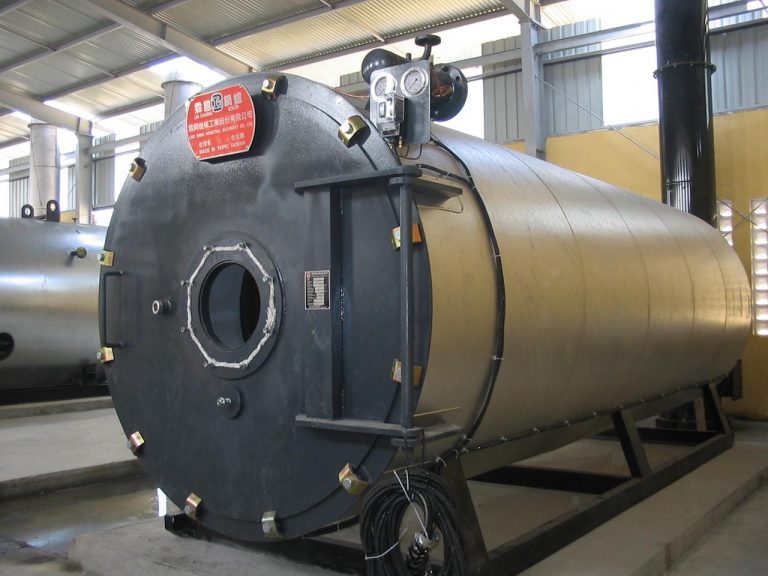

What is a thermal oil furnace?
Thermal oil furnace, also known as heat transfer oil furnace, uses a chain-grate combustion chamber to burn fuel. The energy generated from the fuel combustion process will heat the heat transfer oil. The temperature of the oil after heating can vary. Can reach up to 400oC. After heating, the oil will be sent to heat-using equipment in industrial production. However, in industry, thermal oil furnaces are only used for indirect heat exchange systems, meaning the oil will pass through heat exchangers at heat-using equipment and then be returned to the oil furnace for heating. The heat rises again, so the oil will circulate to complete a closed cycle. Industrial chain grate thermal oil furnaces can reach a capacity of up to 18 GCal/hour. Technical characteristics:
- Boiler technology is calculated, designed, manufactured and installed according to ASME standards.
- Installed heat capacity: 1,000,000 ÷ 16,000,000 kcal/hour.
- Working temperature: 400°C
- Working pressure: 4-15 bar
- Fuel used: Indonesian coal, Biomass…
- Efficiency of thermal oil furnace: > 80%
- Heat transfer fluid: Liquid oil or evaporated oil.
Structure of thermal oil furnace
1. Boiler (Burner): This is where fuel (like oil or gas) is burned to create a heat source. Boilers usually have a solid structure and can withstand high pressure and temperature.
2. Thermal Oil Tank: This is where thermal oil is stored, a heat transfer substance with good heat storage and transfer ability. Thermal oil tanks are typically made from stainless steel or carbon steel, and may have a heating system to maintain a stable temperature.
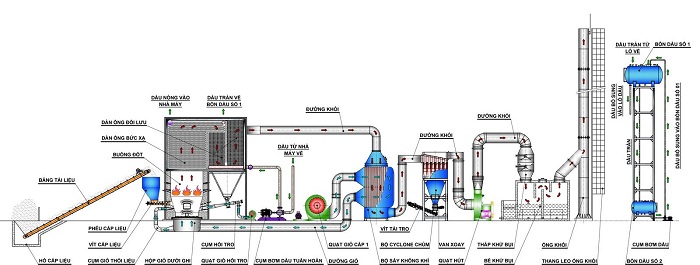
3. Heat Transfer System: Heat pipe system consists of pipes and connecting parts to transfer heat from thermal oil in the tank to the process or system that needs to use heat. The tubes are typically made from stainless steel or carbon steel, and may have external insulation to keep heat from being lost during heat transfer.
4. Temperature Control Devices: These are temperature control parts in the thermal oil furnace, including temperature controllers and temperature sensors. They are used to maintain a stable temperature and control heat transfer according to specific requirements.
5. Safety and Protection System: Thermal oil furnaces need to be equipped with safety and protection devices such as safety valves, pressure reducers, fire and explosion protectors and pressure reducers. pressure. These devices ensure safety during operation and prevent potential problems such as overpressure or risk of fire and explosion.
6. Valves and Control Components: Thermal oil furnaces need a system of valves and control components to regulate the flow of thermal oil and control the heat transfer process. Valves are used to open or close the thermal oil flow, and controls help regulate temperature and pressure as required.
Structural characteristics of thermal oil furnace
Thermal oil furnaces used in industrial production usually include the following main parts:
- Fuel supply system: Designed to operate automatically or semi-automatically. This part supplies fuel to the thermal oil furnace thanks to small equipment such as scoops, screw conveyors, fuel hoppers, etc.
- Combustion chamber – charcoal furnace: This is the part responsible for burning fuel and absorbing heat to effectively serve the heating process.
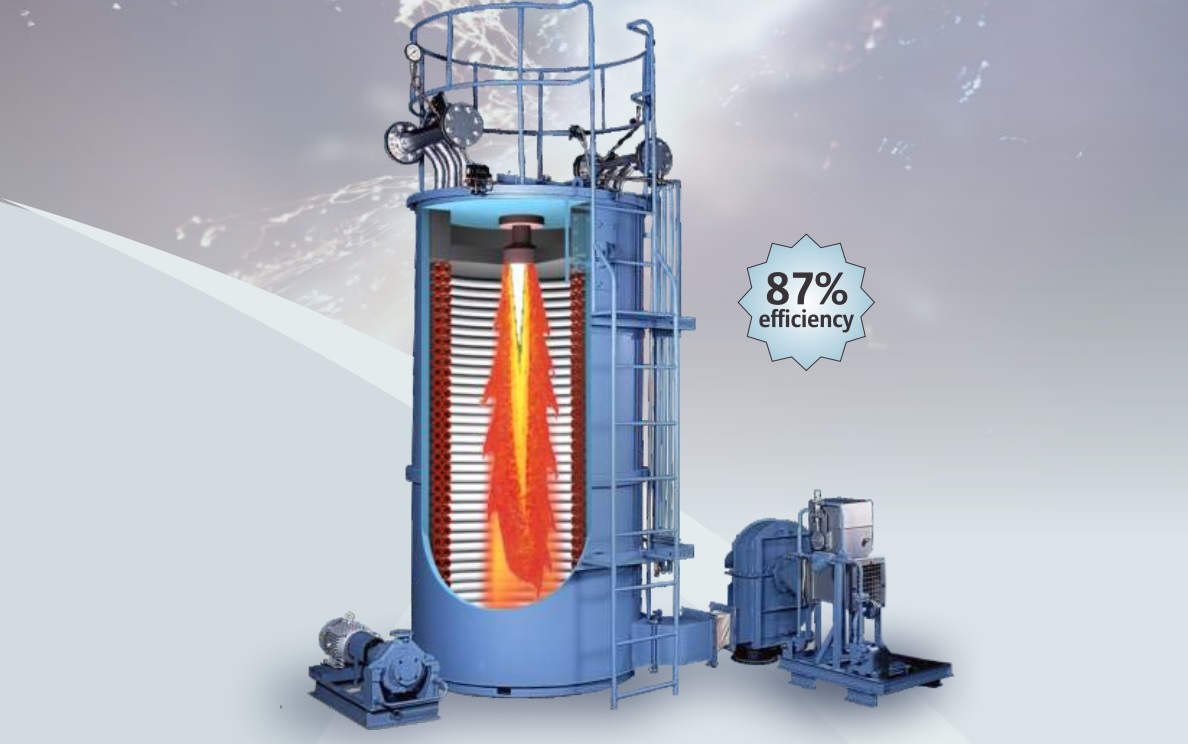

- Air heat recovery unit: Responsible for taking full advantage of the heat source from the exhaust gas, helping to increase the working efficiency of the thermal oil furnace.
- Dust filtration system: Not only is it capable of filtering dry dust up to 99%, but this part is also capable of using a bag dust filtration system, ensuring emissions meet prescribed standards throughout operation.
- Exhaust fan and chimney: After the exhaust gases are filtered through the system, this part will suck them in and push them out into the outside environment.
Operating principle of thermal oil furnace
The operating principle of a thermal oil furnace is quite simple but very effective. The system heats oil (or a heat-resistant liquid) through the combustion chamber. This oil then circulates through pipes and transfers heat to heat exchangers in the plant.
Thermal oil: Heated to high temperatures without increasing pressure, the oil still maintains safety and stability when transferring heat.
Oil circulation system: After the oil has exchanged heat at the necessary points, the oil returns to the furnace to be reheated, helping to maintain a constant temperature throughout operation.
Automatic controller: The control system automates the combustion and oil circulation process, ensuring optimal operating efficiency.
In addition, thermal oil furnaces are capable of burning multiple fuels such as biomass, diesel, and gas, giving users flexibility in choosing fuel supplies, minimizing operating costs and ensuring continuity. in production.




